The pros and cons of a fat adapted diet for athletes
Read time: 5 minutes, 30 seconds.
A fat-adapted athlete is an athlete who has trained their body to efficiently use fat instead of carbohydrates as fuel. This occurs through a combination of dietary changes, training strategies, and lifestyle modifications that help the body become more efficient at burning fat for energy.
When an athlete is fat-adapted, they feel like they have higher energy levels than when they relied primarily on carbohydrates. This is because their body is able to efficiently use fat as a fuel source. And fats provide a more sustained source of energy compared to carbohydrates.
Also Read: Fueling Your Performance: Why Carbohydrates Matter in Sports Nutrition
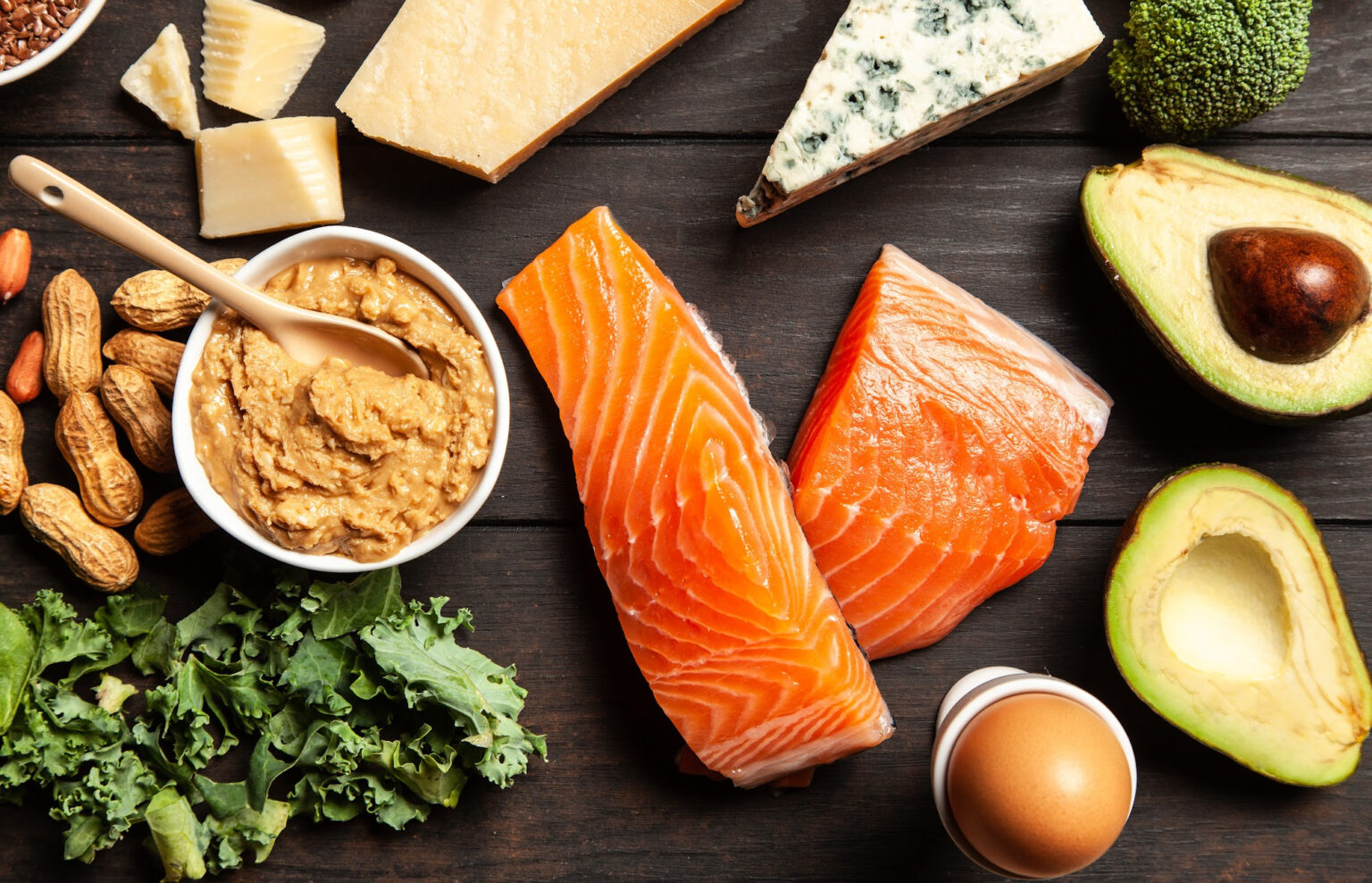
To become fat-adapted, athletes typically follow a high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-carbohydrate diet. Often called the ketogenic diet because it pushes the body into ketosis. Ketosis is essentially the metabolic state that burns fat instead of carbohydrates. This occurs when the body is deprived of glucose, which is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. In the absence of glucose, the liver produces molecules called ketones from stored fat, which can be used by the body as an alternative fuel source.
Becoming a fat-adapted athlete can have benefits for endurance sports such as running, cycling, and triathlon, where sustained energy is important for optimal performance.
Further Reading: A Comprehensive Guide to Nutrition for Endurance Athletes
Athletes who rely on short bursts of energy, such as sprinters or weightlifters, may not benefit as much from being fat-adapted as endurance athletes do. This is because short bursts of energy rely primarily on glycogen (the stored form of glucose), which is derived from carbohydrates, rather than on fat.
In other words, since the process of metabolizing fats for energy is slow in comparison to carbohydrates, many athletes that rely on a quick supply of energy may not see a benefit to performance. In fact, they may see the opposite effect which includes fatigue, dizziness, and muscle weakness.
It’s important to note that this approach may not be suitable for all athletes and should be carefully evaluated by a qualified sports nutritionist or healthcare professional. This is where I can help you. I can create the right diet and training plan for your goals. You can check out my services here.
The ketogenic diet has been shown to have various health benefits, such as weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and reduced inflammation. Some studies have also suggested that the ketogenic diet may benefit athletes by improving their endurance, increasing their fat-burning ability, and reducing their dependence on carbohydrates during exercise.
The biggest criticism of the ketogenic diet is the consumption of high levels of saturated fat. Saturated fat is a type of fat found in animal products such as meat, butter, and cheese, as well as in some plant-based oils like coconut oil. While some saturated fat is necessary for the body to function properly, excessive intake can contribute to the buildup of cholesterol in the arteries, which can lead to heart disease and other health problems.
Further Reading: Embracing Healthy Fats for Optimal Athletic Performance
In the context of the ketogenic diet, it’s important to choose healthy sources of fat and to balance saturated fat intake with other types of fat, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. This can be achieved by including healthy sources of fat in the diet, such as nuts, seeds, avocado, and olive oil, and by limiting the intake of high-fat animal products like fatty cuts of meat and full-fat dairy.
If you’re interested in trying out the ketogenic diet for athletic performance, here are some do’s and don’ts to consider.
DO consume more water and electrolytes than usual.
The ketogenic diet has been associated with an increased risk of muscle cramps, which can be attributed in part to changes in electrolyte balance. Electrolytes are minerals such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium that play important roles in muscle function, nerve transmission, and fluid balance in the body. When following a ketogenic diet, the body may excrete more electrolytes through the urine due to the lower carbohydrate intake, which can lead to imbalances and an increased risk of muscle cramps.
Further Reading: Importance of Electrolytes for Sports Performance
To prevent muscle cramps and maintain electrolyte balance while on a ketogenic diet, it’s important to ensure adequate intake of electrolytes through dietary sources or supplementation. Foods that are high in electrolytes include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and seafood. Additionally, adding salt to food or consuming salted broths can help increase sodium intake. Potassium can be obtained from foods such as avocado and spinach, while magnesium can be found in nuts, seeds, and dark chocolate. If needed, electrolyte supplements can also be taken to ensure adequate intake.
DO consume a ton of fiber.
Consuming enough fiber on the ketogenic diet can be challenging, as many high-fiber foods are also high in carbohydrates. However, fiber is an essential nutrient that plays a key role in maintaining digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and certain types of cancer. Therefore, it’s important to prioritize fiber intake even on a low-carbohydrate diet.
One way to increase fiber intake on the ketogenic diet is to incorporate non-starchy vegetables that are low in carbohydrates but high in fiber, such as leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, and zucchini. These vegetables can be included in salads, stir-fries, and other dishes to increase fiber content. Additionally, nuts and seeds, such as almonds and chia seeds, are also good sources of fiber and can be included in the diet in moderation. Finally, taking a fiber supplement such as psyllium husk can also help ensure adequate fiber intake on the ketogenic diet.
DON'T consume artificial sweeteners.
When following a ketogenic diet, many people turn to artificial sweeteners as a low-carbohydrate alternative to sugar. While these sweeteners may seem like a good option, there are several reasons why you may want to avoid them.
First, some studies have suggested that artificial sweeteners may disrupt the body’s natural ability to regulate blood sugar levels, potentially leading to insulin resistance and other metabolic disorders. This can be particularly problematic for those following a ketogenic diet, as insulin resistance can make it more difficult to achieve and maintain a state of ketosis.
Many artificial sweeteners are associated with negative side effects such as headaches, gastrointestinal problems, and allergic reactions. While not everyone will experience side effects, they can be significant for those who are sensitive to these compounds. Instead of relying on artificial sweeteners, it may be better to use natural sweeteners such as stevia or monk fruit, which are low in carbohydrates and have fewer potential side effects.
DON'T rely on processed or packaged foods.
Avoiding processed foods is an important aspect of a healthy diet, including the ketogenic diet. Because of its popularity, many processed food companies are jumping on the “keto train.” These processed foods are often high in unhealthy fats, and hidden sugars, which can make it difficult to achieve and maintain a state of ketosis. Processed foods also contain artificial preservatives, flavorings, and other additives that can have negative effects on health.
Also Read: My Strategy for Determining Your Ideal Diet and Sticking to It
Instead of relying on processed foods, it’s important to focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fresh vegetables, high-quality proteins, and healthy fats. This not only supports a ketogenic lifestyle but also ensures that you are getting the essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients (like fiber!) your body needs to function properly. By preparing your meals from scratch and avoiding packaged or pre-made foods, you can have more control over the ingredients in your diet and ensure that you are making choices that support your health and well-being.
In summary...
The ketogenic diet is a popular and effective dietary approach that can provide a variety of health benefits and has the potential to improve athletic performance. But, it can also significantly hinder athletic performance as well – especially for short-burst athletes. For those that do find benefit from it, it’s important to note that there’s a right and a wrong way to doing.
By reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, it can help the body enter a state of ketosis, which can promote weight loss, improve blood sugar control, and enhance cognitive function. Make sure you approach the ketogenic diet with caution and ensure that you are getting adequate nutrients to avoid potential side effects. Make sure that you are consuming plenty of nature-based fats, whole-foods (especially non-starchy vegetables), and electrolytes. And just like any diet, make sure you’re avoiding processed foods and artificial sweeteners.

Adult Athletes Playbook
A Guide to Peak Performance and Athletic Longevity
This playbook will help you develop and implement a personalized game plan for improving athletic performance.













One Comment
Pingback: